Degenerative Spine Treatment
- Home
- Degenerative Spine Treatment
Degenerative Spine Treatment in Pimpri Chinchwad
“Most people with degenerative disc disease can manage their ongoing pain, as well as more painful flare episodes, with conservative (non-surgical) care.”
What is Degenerative Disc Disease?
Despite its name, degenerative disc disease is not a disease; it is simply a term referring to the wearing down of the spinal discs that may occur as part of the body’s natural aging process. The spinal discs separate the vertebrae, the interconnected bones of which the spine is made of; these discs allow the spine to move smoothly. Degenerative disc disease can affect any part of the spine; however, it typically affects the neck (cervical) and lower back (lumbar) areas.
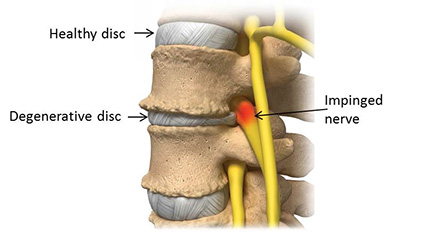
Causes of Degenerative Disc Disease:
Degenerative disc disease almost always occurs as a result of aging. In some people, the natural aging process simply causes the spinal discs to break down, or degenerate. These changes include fluid loss within the discs, reducing their overall flexibility, and tears in the discs, causing them to bulge or rupture. In some people, degenerative disc disease occurs after developing a herniated disc, typically caused by an injury.
As with many other conditions, degenerative disc disease is more apt to develop in people that smoke or are obese. It is therefore important to quit smoking and develop an active, healthy life to lower your chances of developing degenerative disc disease and many other conditions.
Symptoms of Degenerative Disc Disease:
The symptoms of degenerative disc disease vary from person to person, depending on the affected area. Individuals suffering from this condition may experience pain in their neck, back, arm, leg, or buttocks. Some people may experience no pain at all from this condition, in which case it remains unnoticed. Individuals experiencing pain in any of the aforementioned areas should see their doctor to verify its cause.
Diagnosing Degenerative Disc Disease:
To diagnose degenerative disc disease, your doctor will perform a full physical exam and review your medical history. The examination will entail inspecting the affected area for tenderness, numbness, decreased range of motion, and pain during motion, among other factors. In certain cases, x-rays may be utilized to obtain a clearer view of the affected area.
Treatment:
Nonsurgical Treatment
- Pain control focuses on reducing pain from the damaged disc and helping you return to your daily activities. Methods of pain control may include anti-inflammatory medications, manual manipulation, steroid injections, electrical stimulation, back braces or heat/ice therapy.
- Physical therapy can help stretch and strengthen the right muscles to help the back heal and reduce the frequency of painful flare-ups.
- Lifestyle modifications, such as changing your posture, losing weight or giving up smoking, can sometimes help reduce stress on the damaged disc and slow down further degeneration.
Surgical Options
Surgical options are available for people who experience severe pain or significant loss of function and don’t respond to other treatments. The surgery may involve removal and replacement of the whole or a part of the affected disc (partial or total disc replacement). Another option is disc removal (discectomy) with spinal fusion that reduces the movement in the damaged spine segment.

