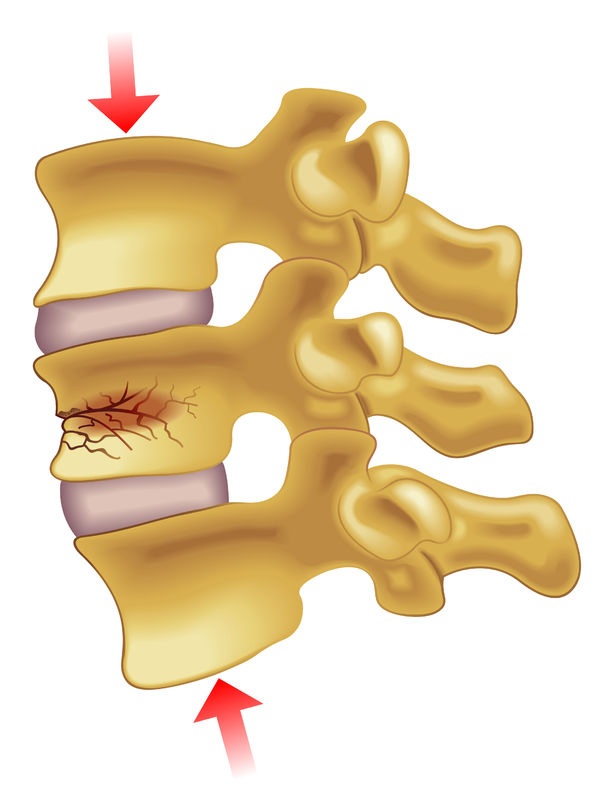
Spinal Fractures
- Home
- Spinal Fractures
Spinal fractures Treatment in PCMC
“Spinal fractures can be caused by accidents or occur as a result of osteoporosis. Surgery may be needed for severe cases.”
Spinal fractures are different than a broken arm or leg. A fracture or dislocation of a vertebra can cause bone fragments to pinch and damage the spinal nerves or spinal cord. Most spinal fractures occur from car accidents, falls, gunshot, or sports. Injuries can range from relatively mild ligament and muscle strains, to fractures and dislocations of the bony vertebrae, to debilitating spinal cord damage. Depending on how severe your injury is, you may experience pain, difficulty walking, or be unable to move your arms or legs (paralysis). Many fractures heal with conservative treatment; however severe fractures may require surgery to realign the bones.
Spinal fractures symptoms are:
Symptoms of a spinal fracture vary depending on the severity and location of the injury. They include back or neck pain, numbness, tingling, muscle spasm, weakness, bowel/bladder changes, and paralysis. Paralysis is a loss of movement in the arms or legs and may indicate a spinal cord injury. Not all fractures cause spinal cord injury and rarely is the spinal cord completely severed.
Who is affected?
- 80% of patients are aged 18-25 years
- Men are 4 times more likely to have a traumatic spinal fracture than women
Treatment options:
Medical Treatment
Most fractures are treated with immobilization in a brace or corset for up to 12 weeks. Bracing helps to reduce pain and prevent deformity.
Surgical Treatment
Severe cases may require surgery.
Vertebroplasty is a new surgical procedure that may be used to treat compression fractures. In this procedure, the surgeon inserts a catheter into the compressed vertebra. The catheter is used to inject the fractured vertebrae with bone cement, which hardens, stabilizing the vertebral column. This procedure has been shown to reduce or eliminate fracture pain, enabling a rapid return to mobility and preventing bone loss due to bed rest. However, it does not correct the spinal deformity.
Kyphoplasty involves inserting a tube into the vertebral column under X-ray guidance, followed by the insertion of an inflatable bone tamp. A tiny incision is made in the back. Once inflated, the tamp restores the vertebral body back toward its original height, while creating a cavity to be filled with bone cement. The cement seals off cracks and cavities, and prevents the vertebra from re-collapsing. After the cavity is filled, the tube is removed and the incision stitched. Since August 1998, hundreds patients have been treated at The Cleveland Clinic with kyphoplasty.